Archives¶
Here are just backup information for retired resources.
IDF¶
A PanDA setup for the Rubin DP0.2 exercise consists of several components including a test PanDA server instance located at CERN, two Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters deployed in the Google based Interim Data Facility (IDF), submission node in the Google Cloud and other components. In this document we will describe only several components from the whole setup (Fig. 1) facing end users.
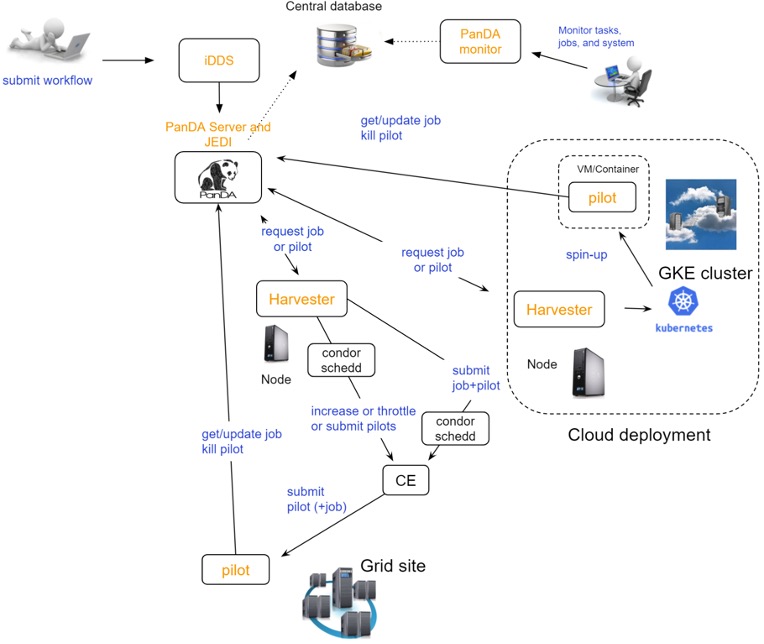
Fig 1. System component diagram
GKE queues¶
There are 7 production queues pre configured in the IDF GKE in order to match particular job requirements:
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST. For jobs that are not sensitive to node preemption and requiring no more than 3200MB of RAM. The majority of Rubin jobs run on this queue.
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_HIMEM. For jobs requiring more than 3200MB but less than 18000MB of RAM, this high memory preemption queue can be used.
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_EXTRA_HIMEM. This is a queue for extremely memory-demanding jobs requiring up to 220000MB of memory. If a submitting task requests RAM more than the capability of the DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_HIMEM queue, the job becomes assigned to this queue.
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_MERGE. This is a special queue to run merge jobs finalizing each submitted workflow. This queue has been excluded from the automatic PanDA brokerage, and tasks are assigned using the queue definition parameter in the Rubin BPS submission YAML.
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_HIMEM_NON_PREEMPT. We have experimentally observed that jobs lasting more than 12 hours have a low probability of success due to nodes preemption. This significantly impacts the duration of the workflow run because it takes a few days of running and failing attempts to reach the retry attempt, which will finally survive. That long-lasting retry attempts with a low survival rate also negatively impacts the cost-efficiency. To increase the chances for such durable jobs to finish from the first attempt, we created a special non-preemptive queue. In terms of RAM, the queue is equivalent to the DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_HIMEM.
DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_EXTRA_HIMEM_NON_PREEMPT. Same use case as the queue above. In terms of RAM, the queue is equivalent to the DOMA_LSST_GOOGLE_TEST_EXTRA_HIMEM.
DOMA_LSST_DEV. This cluster is used for testing developments before deploying them into the production environment.
The PanDA server performs automatic landing tasks in the appropriate queue using the memory requirements information. There are few associated configuration parameters should be defined in the YAML:
computing_cloud: LSST
pipetask:
measure:
requestMemory: 8129
mergeMeasurements:
requestMemory: 4096
fileDistributionEndPoint: s3://butler-us-central1-panda-dev/hsc/{payload_folder}/{uniqProcName}/
s3_endpoint_url: https://storage.googleapis.com
...
The first parameter (computing_cloud) defines the PanDA cloud associated with the IDF. The requestMemory setting defines the RAM request per task type.
SDF¶
Here are queues for the SDF cluster. These queues are brokeroff. Users need to
specify them in order to submit jobs to them.
PanDA Queue |
slurm queue |
minRSS |
maxRSS |
Harvester mode |
Brokerage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SLAC_Rubin_SDF |
rubin |
0GB |
4GB |
pull |
off |
SLAC_Rubin_SDF_Big |
rubin |
0GB |
220GB |
push |
off |